Difference Between PM2.5 and PM10 – How They Affect Your Health
Air pollution has become a major concern in urban and industrial areas, and understanding PM2.5 and PM10 is critical for protecting your health. These tiny particles, often invisible to the naked eye, can penetrate deep into our respiratory system, causing a range of health problems. In this blog, we’ll explore the difference between PM2.5 and PM10, their sources, and their impact on human health.
What Are PM2.5 and PM10?
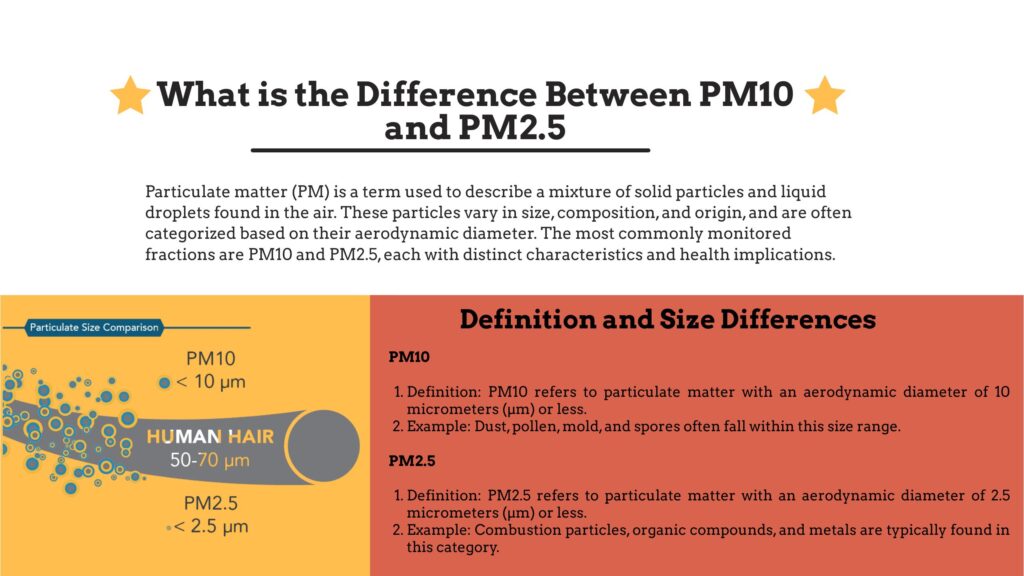
PM2.5 and PM10 are terms used to describe particulate matter (PM) suspended in the air. Particulate matter consists of microscopic solids or liquid droplets that can be inhaled into the lungs.
PM2.5 refers to particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or smaller. These particles are so tiny that they can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream.
PM10 refers to slightly larger particles with a diameter of 10 micrometers or smaller. While larger than PM2.5, PM10 can still be inhaled and affect the respiratory system.
Both PM2.5 and PM10 are harmful, but PM2.5 is considered more dangerous because it can reach deeper parts of the lungs and the circulatory system.
Sources of PM2.5 and PM10
Understanding the sources of PM2.5 and PM10 is crucial to controlling exposure.
Common sources of PM2.5:
Vehicle exhaust fumes
Industrial emissions
Burning of fossil fuels and biomass
Smoke from wildfires
Secondary particles formed in the atmosphere
Common sources of PM10:
Dust from roads and construction sites
Pollen and mold spores
Sea salt or soil particles
Industrial processes
Both PM2.5 and PM10 can originate from natural and human-made sources. However, urban environments tend to have higher concentrations due to traffic and industrial activity.
The Difference Between PM2.5 and PM10
While both are particulate matter, the main difference between PM2.5 and PM10 lies in particle size and health impact:
| Feature | PM2.5 | PM10 |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | ≤ 2.5 micrometers | ≤ 10 micrometers |
| Health Impact | Can penetrate deep into lungs and bloodstream | Affects upper respiratory tract mainly |
| Visibility | Usually invisible | May appear as dust in sunlight |
| Common Sources | Combustion, industrial emissions | Dust, pollen, construction |
By understanding the difference, individuals can take informed steps to protect themselves from PM2.5 and PM10 exposure.
How PM2.5 and PM10 Affect Your Health
Exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 can lead to short-term and long-term health issues:
Health Effects of PM2.5:
Respiratory problems like asthma, bronchitis, and reduced lung function
Cardiovascular diseases due to particles entering the bloodstream
Premature death in people with heart or lung conditions
Increased risk for children and elderly
Health Effects of PM10:
Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat
Allergic reactions
Coughing and sneezing
Aggravation of pre-existing respiratory conditions
Studies show that PM2.5 and PM10 exposure is linked to chronic health issues. Indoor air quality monitors can help detect these particles to reduce exposure effectively.
Indoor vs Outdoor PM2.5 and PM10
While most people are concerned about outdoor air pollution, indoor PM2.5 and PM10 can also be significant:
Cooking smoke, incense, tobacco, and dust contribute to indoor PM2.5 and PM10
Poor ventilation increases particle concentration indoors
Indoor air quality can be monitored using PM2.5 and PM10 sensors, which provide real-time data to protect your family
How to Protect Yourself from PM2.5 and PM10
Taking steps to reduce exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 is essential for long-term health:
Use air purifiers equipped to filter PM2.5 and PM10
Monitor air quality using reliable sensors for PM2.5 and PM10
Avoid outdoor activities during high pollution days
Maintain proper ventilation in homes and offices
Keep indoor spaces clean to reduce dust and particulate matter
PM2.5 and PM10 Monitoring Solutions
Modern technology allows real-time monitoring of PM2.5 and PM10. Homeowners and businesses can install air quality sensors to:
Track particulate levels indoors and outdoors
Receive alerts when PM2.5 and PM10 exceed safe limits
Take preventive action to reduce exposure
You can explore PM2.5 and PM10 sensors on Jayesh Traders to maintain a healthy indoor environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Which is more dangerous, PM2.5 or PM10?
PM2.5 is more harmful because it can penetrate deeper into the lungs and bloodstream.
Q2: How can I measure PM2.5 and PM10 at home?
Use indoor air quality monitors designed to detect PM2.5 and PM10.
Q3: Can PM2.5 and PM10 cause long-term health issues?
Yes, prolonged exposure can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
Q4: How to reduce PM2.5 and PM10 indoors?
Improve ventilation, use air purifiers, and monitor air quality using PM2.5 and PM10 sensors.
Conclusion
Understanding PM2.5 and PM10 is vital for protecting your health. Both particulate matters can cause respiratory and cardiovascular issues, but PM2.5 poses a higher risk. By monitoring and taking preventive measures, such as using air purifiers and sensors, you can significantly reduce exposure to these harmful particles.
Stay informed, protect your health, and explore reliable PM2.5 and PM10 monitoring solutions at Jayesh Traders.




